http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heck_reaction
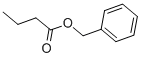
This reaction shows how it is completed in the presence of a organopalladium catalyst. The halide which can consist of (Br,Cl) usually is a aryl, benzyl, or vinyl compound and the alkene contains at least one proton and is usually proton-deficient. The base consist of triethylamine, potassium carbonate, or sodium acetate. In addition, the catalyst contains palladium chloride or palladium acetate with the ligand containing triphenylphosphine or BINAP.
After reading over the article I concluded that they were examining the chelation effects by moving the oxidizing functionality away from the allylic position. Under the oxidized conditions, the acidic Heck reactions coupld rapidly synthesize 4-arylated-but-2-enoates and -enone just as single olefin isomers.
In conclusion, they showed a intermolecular Heck reaction coorelating to olefin in the cross-coupling method. The general catalyst Pd/bis-sulfoxide complex can catalyzes a chelate-controlled oxidative Heck reaction. In addition to this, electrophilic catalyst is senstitive to the chelation effect from oxygen and nitrogen which result in the regioselectivities for the olefin insertion.The reaction below shows the specific reaction mechanism for the Heck reaction.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heck_reaction
I was not able to add the pictures from the publication however, you can read the article as well as seeing the results at http://www.scs.illinois.edu/white/pubs/pub11.pdf